In the competitive world of business, one of the most critical metrics for understanding long-term customer profitability is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). CLV allows businesses to determine the total revenue a company can expect from a single customer account over the duration of their relationship.

More importantly, it helps companies make informed decisions on customer acquisition, retention strategies, and overall marketing budgets. Understanding how to calculate customer lifetime value and why it matters is essential for long-term business success.
This article will walk you through everything you need to know about Customer Lifetime Value, including its definition, importance, models, formulas, metrics, examples, and strategies to improve it.
Table of Contents
What is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)?
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), also referred to as Lifetime Value (LTV), is the projected revenue that a customer will generate during their entire relationship with a business.
It includes the customer’s total purchases, the frequency of those purchases, and how long they continue to purchase from the business. CLV helps businesses measure the value of their customer relationships, enabling them to understand the return on investment (ROI) from customer acquisition efforts.

CLV is more than just an arbitrary number—it provides actionable insights into a company’s marketing strategy, helping to answer questions like: How much should you spend on acquiring new customers? Which customers are most valuable? How can you retain high-value customers?
Why is Customer Lifetime Value Important?
CLV is a crucial metric for several reasons, ranging from financial forecasting to shaping customer acquisition and retention strategies. Here are a few key reasons why understanding CLV is so important for a business:
1. Optimizing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Knowing your CLV allows you to compare it against your customer acquisition cost (CAC). If it costs you more to acquire a customer than you will earn from them over their lifetime, your business model is unsustainable.
CLV helps you optimize your marketing spend by ensuring that you are not overspending to acquire low-value customers.
2. Focusing on Customer Retention
It’s often said that retaining an existing customer is much cheaper than acquiring a new one. By understanding the CLV of different customer segments, businesses can focus their efforts on retaining high-value customers. Small improvements in customer retention can lead to significant increases in revenue.
3. Increasing Revenue Predictability
CLV helps businesses make more accurate revenue projections. By knowing how much a customer is likely to spend over their lifetime, you can estimate future cash flows and more effectively plan for growth.
4. Segmentation and Personalization
Knowing which customers have the highest CLV allows companies to segment their customer base and tailor their marketing efforts accordingly. High-CLV customers may receive personalized offers, premium services, or exclusive promotions, increasing their satisfaction and loyalty.
5. Strategic Decision-Making
Whether you’re deciding on pricing strategies, launching new products, or expanding into new markets, CLV provides valuable insights that can influence these key decisions.
For example, businesses can use CLV to set pricing that maximizes long-term profitability rather than focusing solely on short-term gains.
Customer Lifetime Value Models
There are several different models for calculating Customer Lifetime Value, depending on how granular or simple a business wants to be. These models range from basic calculations to more complex methods that consider various factors like customer churn rate, gross margin, and discount rates.
1. Historical CLV
This is one of the simplest methods of calculating CLV. Historical CLV calculates the sum of the gross profits from all previous purchases made by a customer. However, it doesn’t provide insights into future purchasing behavior, making it less useful for long-term planning.
2. Predictive CLV
Predictive CLV estimates a customer’s future value based on past behavior, purchase history, and other factors like browsing patterns, social interactions, and engagement with the brand. Machine learning algorithms are often used to improve the accuracy of this model.
3. Cohort-Based CLV
Cohort analysis groups customers based on when they made their first purchase or by other specific criteria, allowing companies to calculate CLV for different customer segments. This helps businesses understand how different acquisition channels or marketing campaigns impact long-term value.
4. Subscription-Based CLV
For businesses with recurring revenue models, such as subscription services, CLV is often calculated based on the monthly or annual recurring revenue (MRR or ARR). This model includes churn rate and customer lifetime in its calculation.
Customer Lifetime Value Formula
The formula for calculating Customer Lifetime Value can vary, but the most commonly used one is:
CLV = (Average Purchase Value) x (Average Purchase Frequency Rate) x (Customer Lifespan)
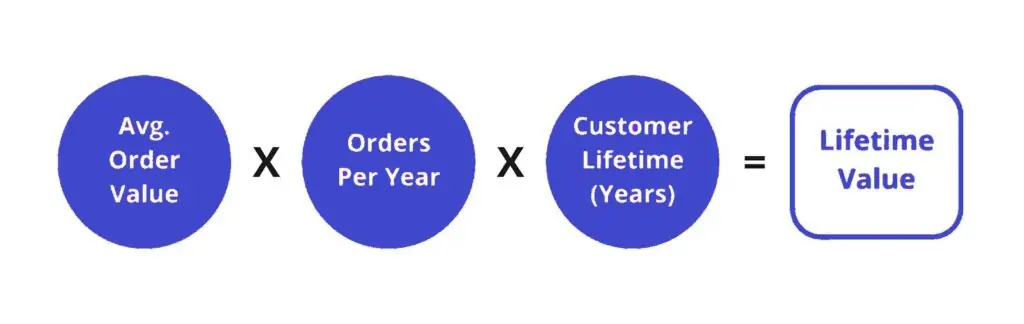
Breaking it down:
- Average Purchase Value (APV): The total revenue divided by the number of purchases.
- Average Purchase Frequency Rate (APFR): The average number of purchases made by a customer within a given time frame.
- Customer Lifespan (CL): The average time a customer remains loyal to the business, usually measured in years or months.
For businesses with recurring revenue models, the formula might look like:
CLV = (Average Revenue Per User) / (Churn Rate)
This formula is more appropriate for subscription-based businesses, where churn rate plays a more critical role in determining CLV.
How to Calculate Customer LTV
Now that we understand the formulas, let’s walk through the step-by-step process of calculating customer LTV.
1. Determine the Average Purchase Value
Calculate the total revenue generated from all customers and divide it by the number of purchases. For example, if your business generated $100,000 from 2,000 purchases, the APV would be $50.
2. Calculate the Average Purchase Frequency Rate
Divide the total number of purchases by the number of unique customers. For instance, if your store had 2,000 purchases made by 500 customers, your APFR would be 4.
3. Estimate the Customer Lifespan
To calculate the customer lifespan, divide 1 by the churn rate (for subscription models) or calculate how long, on average, customers continue to purchase from you. For example, if the average customer remains loyal for five years, that is the customer lifespan.
4. Multiply the Three Values
Finally, multiply the APV, APFR, and customer lifespan to arrive at your CLV. For example, if your APV is $50, your APFR is 4, and your customer lifespan is 5 years, your CLV would be:
CLV = 50 x 4 x 5 = $1,000
In this case, the average customer would generate $1,000 over the course of their relationship with your business.
Customer Lifetime Value Metrics
To fully understand CLV, it’s important to track various metrics that impact this calculation. Some key metrics include:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The amount you spend to acquire each customer. A high CAC can significantly reduce the overall profitability of a customer.
- Churn Rate: The rate at which customers stop doing business with you. A high churn rate means a shorter customer lifespan.
- Gross Margin: The profit made from a customer after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS).
- Purchase Frequency: The average number of transactions a customer makes during their relationship with your company.
- Average Order Value (AOV): The average amount a customer spends per transaction. Increasing AOV is one way to increase CLV.
Customer Lifetime Value Example
Let’s take a practical example of calculating CLV for an e-commerce business.
Example:
- Average Purchase Value (APV): $70
- Average Purchase Frequency Rate (APFR): 5 purchases per year
- Customer Lifespan: 3 years
CLV = $70 x 5 x 3 = $1,050
In this example, each customer is expected to generate $1,050 in revenue over their lifetime with the company.
Factors Influencing Customer Loyalty
Following are the points which count as factors, each of which plays a critical role in how customers perceive and engage with a brand.
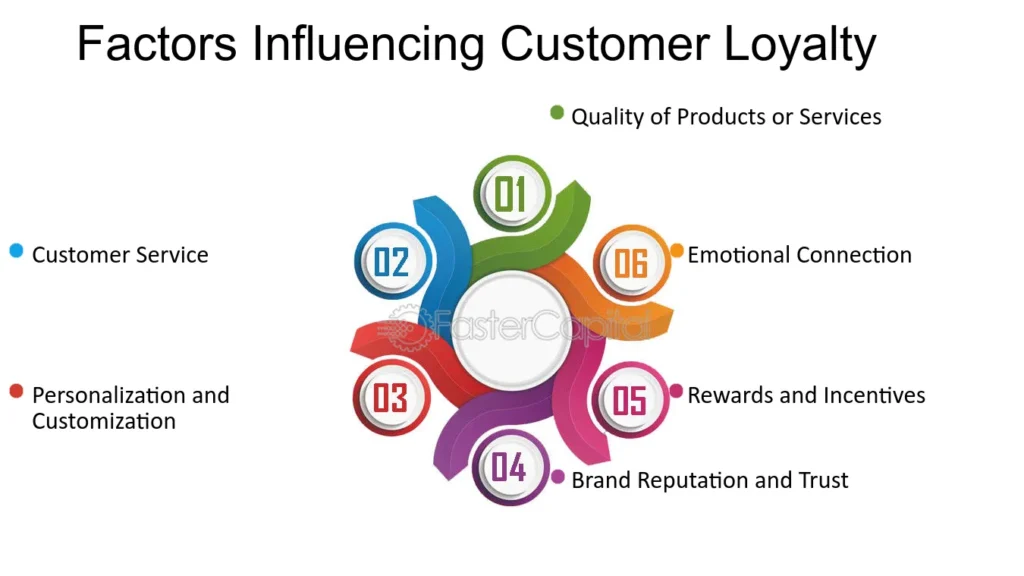
Quality of Products or Services:
Customers remain loyal to brands that consistently deliver high-quality products or services. Reliability, durability, and satisfaction are key attributes that reinforce loyalty.
Customer Service:
Providing exceptional, responsive, and friendly customer service helps build strong relationships with customers, leading to repeat business and long-term loyalty.
Personalization and Customization:
Customers appreciate brands that tailor experiences, products, and communications to their individual preferences. Personalized offers, recommendations, and customized products strengthen the bond between the customer and the brand.
Brand Reputation and Trust:
A brand’s reputation for honesty, reliability, and ethical practices fosters trust. A good reputation encourages customers to remain loyal, knowing that they can count on the brand for consistent quality and service.
Rewards and Incentives:
Loyalty programs, discounts, and special offers give customers a reason to keep coming back. When customers feel valued and rewarded for their loyalty, they are more likely to stay with the brand, Like Starbuck’s loyalty program called Starbucks Rewards
It incentivizes customers to keep returning by offering points for purchases. These points can be redeemed for free drinks, food, and merchandise, making customers feel appreciated and increasing brand loyalty.
Emotional Connection:
Brands that can connect with customers on an emotional level create stronger, more resilient relationships. Whether it’s through shared values, memorable experiences, or a sense of community, emotional engagement keeps customers loyal even in the face of competition.
These six factors form the foundation for a successful customer loyalty strategy, ensuring that customers not only return but also become advocates for the brand.
Tips to Increase Customer LTV
Once you’ve calculated your CLV, the next step is to focus on increasing it. Here are some strategies to boost customer LTV:
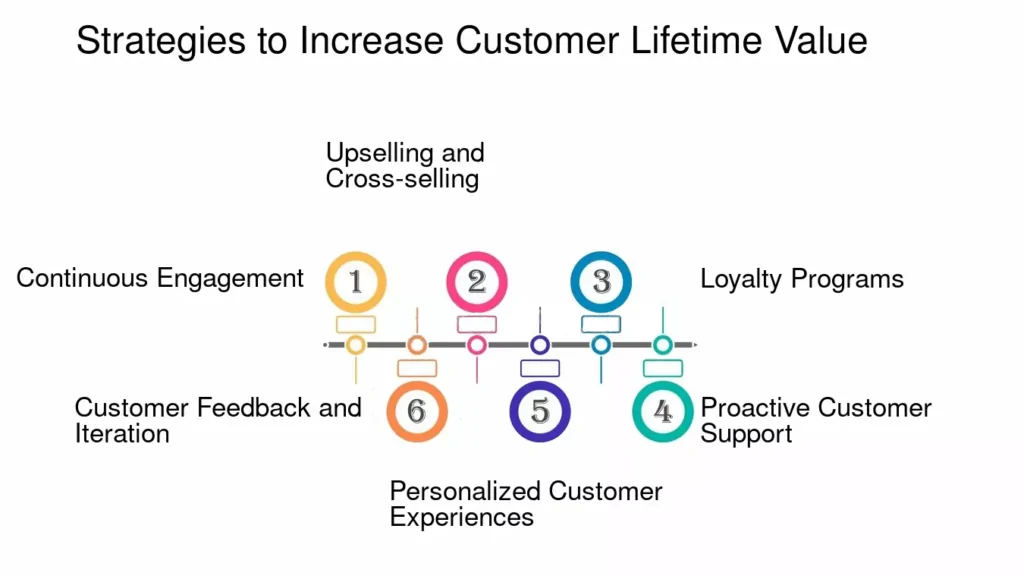
1. Improve Customer Experience
Providing an exceptional customer experience, from easy navigation on your website to stellar customer support, can significantly increase customer loyalty and retention.
2. Upsell and Cross-Sell
Increase the average order value by offering complementary products or encouraging customers to upgrade their purchases. Personalized recommendations based on purchase history can be a powerful tool.
3. Implement Loyalty Programs
Encourage repeat purchases by offering incentives through loyalty programs. Customers who receive rewards for their purchases are more likely to return.
4. Reduce Churn
Identify why customers are leaving and take steps to reduce churn. Offering proactive customer service, personalized follow-ups, and satisfaction surveys can help.
5. Personalize Marketing Efforts
Leverage customer data to send personalized offers, product recommendations, and follow-ups. Personalized marketing increases engagement and loyalty, thereby increasing LTV.
6. Improve Onboarding Process
First impressions matter. Ensuring new customers have a smooth onboarding experience increases the likelihood of long-term retention.
7. Leverage Data Analytics
Use data to identify your highest-value customers and focus retention efforts on them. Offering them exclusive perks or customized experiences can further increase their value to your business.
Closing remarks
Customer Lifetime Value is a fundamental metric that helps businesses understand the long-term profitability of their customer relationships. By accurately calculating CLV, companies can make data-driven decisions regarding marketing spend, customer retention, and overall business strategy.
It provides critical insights into which customers are worth investing in and how to optimize their long-term value. By monitoring CLV and implementing strategies to increase it, businesses can not only grow their revenue but also build lasting relationships with customers that drive sustainable success.






