Getting Ensure Google Indexes Your Website Fast is a crucial step in ensuring it appears in search engine results.
Without proper Ensure Google Indexes Your Website Fast cannot discover and rank your site, leaving your audience unable to find you, regardless of how exceptional your content or services might be.
Whether you run a personal blog, an e-commerce store, or a professional business Ensure Google Indexes Your Website Fast is the foundation of your online visibility and success.
This process involves Google crawling through your site, understanding its content, and storing it in its vast database to display it in relevant search results.
If Google doesn’t index your site, even the most well-crafted pages, optimized keywords, and compelling calls-to-action will remain hidden from potential visitors.
The importance of being indexed cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts your site’s traffic, credibility, and growth.
To help you navigate this vital process, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the essentials of understanding indexing, checking if your site is already indexed, optimizing your pages for seamless indexing, and troubleshooting deeper issues that could be preventing Google from recognizing your site.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced webmaster, mastering these steps is key to ensuring your online presence thrives.
Table of Contents
How to Check if You’re Indexed in Google
Before diving into strategies to get indexed, it’s essential to first determine whether Google has already indexed your website.
Ensuring your site is indexed is the foundation of a successful SEO strategy, as it means Google recognizes and stores your pages in its search database.
Without this step, your content won’t appear in search results, no matter how optimized it may be.
Thankfully, there are several straightforward methods to check if your website is indexed by Google:
1. Search “site:” on Google
One of the simplest ways to check your site’s indexing status is by using Google’s site: operator directly in the search bar.
This operator helps you see which of your site’s pages are currently stored in Google’s index. To use it, enter the following command:
site:yourwebsite.com
Replace “yourwebsite.com” with your domain name. For example, if your website is called example.com, the query would be:
site:example.com
Once you hit enter, Google will display a list of all the pages it has indexed from your website.
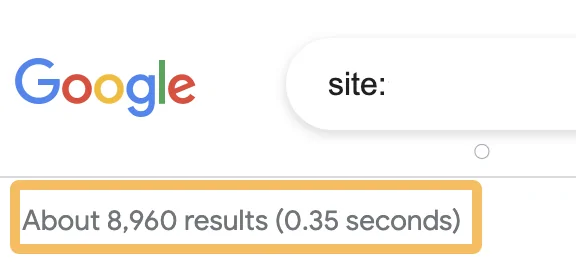
This includes your homepage, blog posts, product pages, and any other indexed content.
If results appear, it means those pages are visible to Google and can show up in search results.
However, if no results are displayed, it indicates that your website has not yet been indexed.
To gain further insights, look at the list of indexed pages to ensure key pages like your homepage and cornerstone content are included.
If you notice important pages are missing, you may need to optimize your site structure or submit them manually.
2. Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is an invaluable free tool provided by Google to help you monitor, manage, and troubleshoot your site’s presence in search results.
Among its many features, it allows you to check your website’s indexing status and identify potential issues that could prevent Google from indexing your pages. To use it effectively:
- Log in to Google Search Console using your Google account.
If you haven’t set it up yet, you’ll need to verify ownership of your website, which can be done through various methods such as DNS settings, HTML files, or tag insertion.
. - Once inside, select the property (your website) you wish to check.
. - Navigate to the “Coverage” report under the Index tab.
This section provides a detailed overview of your site’s indexing status, including how many pages are indexed, how many are excluded, and any errors that may be preventing successful indexing.
.
The “Coverage” report will also highlight warnings such as server errors, blocked resources, or pages marked as “noindex.”
By addressing these issues, you can improve your site’s crawlability and indexing potential.
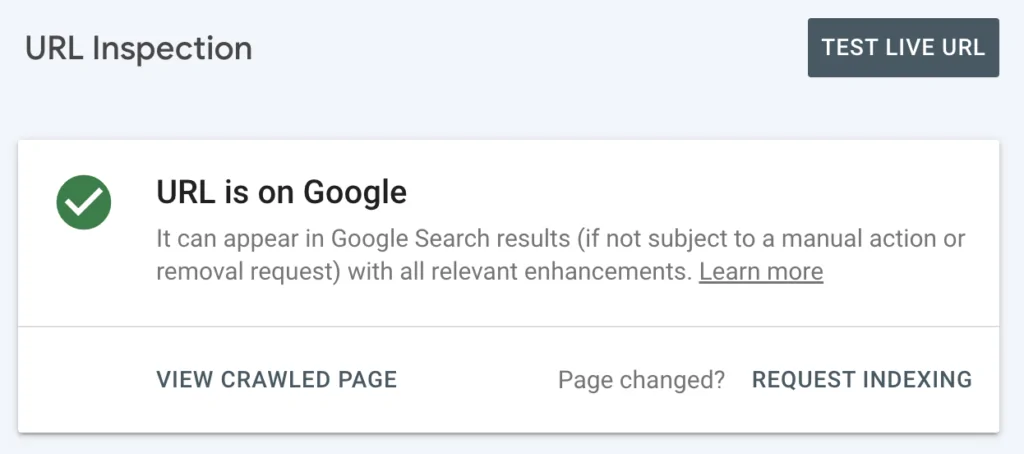
3. URL Inspection Tool
Another powerful feature within Google Search Console is the URL Inspection Tool, which allows you to check the indexing status of specific pages.
If it’s Indexed it will show
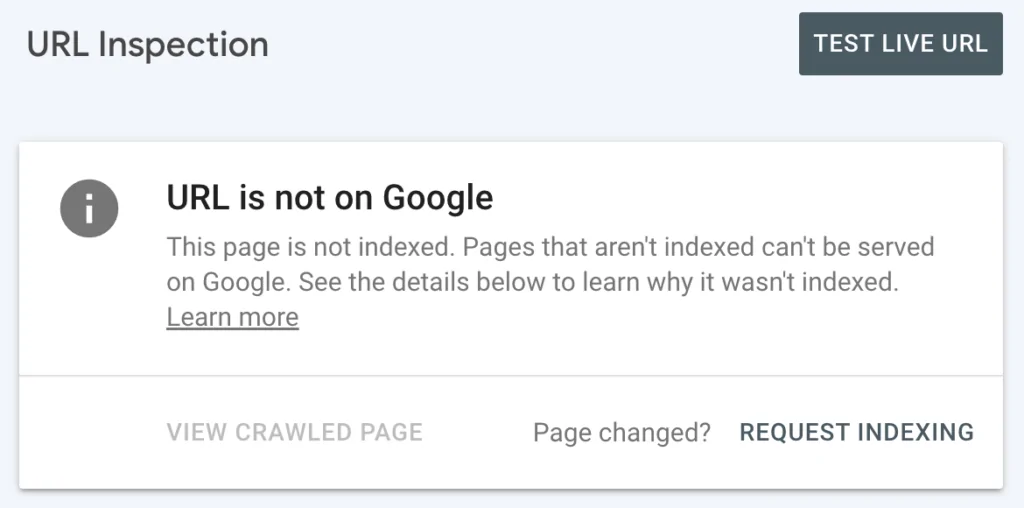
If it’s not Indexed it will show
This is particularly useful if you’ve recently published or updated a page and want to ensure it’s included in Google’s index.
To use the URL Inspection Tool:
- Navigate to the tool in the left-hand menu of Google Search Console
. - Enter the exact URL of the page you wish to check into the search bar.
. - Google will analyze the URL and provide details about its status. If the page is indexed, you’ll see a confirmation message.
If not, the tool will explain why it hasn’t been indexed and offer suggestions for resolving any issues.
.
If the page isn’t indexed, you can click the “Request Indexing” button to prompt Google to review and add it to its index. Keep in mind that this process can take anywhere from a few hours to a couple of days, depending on Google’s crawl schedule.
Why Checking Indexing is Crucial
Regularly checking whether your site or specific pages are indexed helps you identify issues early and ensures that your content is discoverable by users.
If your site isn’t indexed, none of the other SEO efforts you make will matter because your content will remain invisible to search engines.
Tools like the site: operator and Google Search Console not only help you verify indexing but also give insights into potential problems that may need to be addressed to improve your overall search visibility.
By proactively monitoring and managing your site’s indexing status, you’re laying the groundwork for stronger organic performance.
How to Get Indexed by Google
Once you’ve confirmed your site isn’t indexed, follow these steps to ensure Google starts including your pages in its index.
Ensuring proper indexing is the foundation of visibility in search results and critical for driving organic traffic to your site.
1. Request Indexing for Your Homepage
The homepage is typically the gateway to your website’s other pages. It acts as the central hub, making it one of the most crucial pages for indexing.
Here’s how to ensure it gets indexed effectively:
- Access Google Search Console: Log into your Google Search Console account.
. - Use the URL Inspection Tool: In the Search Console dashboard, input your homepage URL into the URL Inspection Tool.
. - Request Indexing: If the tool indicates that your page isn’t indexed, click the “Request Indexing” button.
.
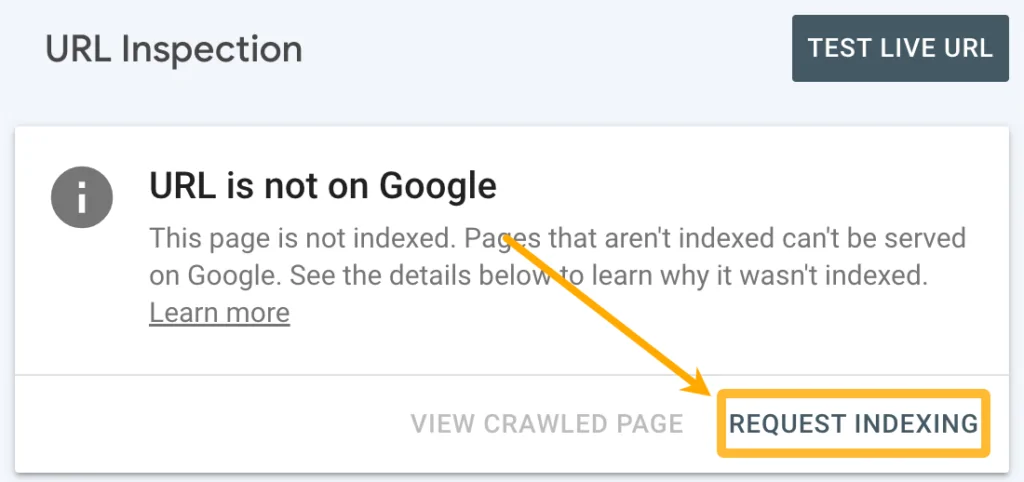
This action prompts Google’s crawler (Googlebot) to visit and evaluate your page for inclusion in its index.
It’s also a good idea to ensure that the content on your homepage is fresh and regularly updated.
Add relevant internal links pointing to key pages on your site, as this will encourage deeper crawling by Google.
2. Create and Submit a Sitemap to Google
A sitemap is a file (usually in XML format) that lists all the significant URLs on your website.
It acts as a roadmap for Google, helping it understand your site structure and prioritize which pages to crawl.
Submitting a sitemap ensures no critical pages are overlooked, even if they’re not well-linked internally.
Steps to Create and Submit a Sitemap:
- Create a Sitemap:
- Use tools such as XML Sitemap Generator or Screaming Frog to generate your sitemap.
. - For WordPress users, plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math offer automatic sitemap creation.
.
- Use tools such as XML Sitemap Generator or Screaming Frog to generate your sitemap.
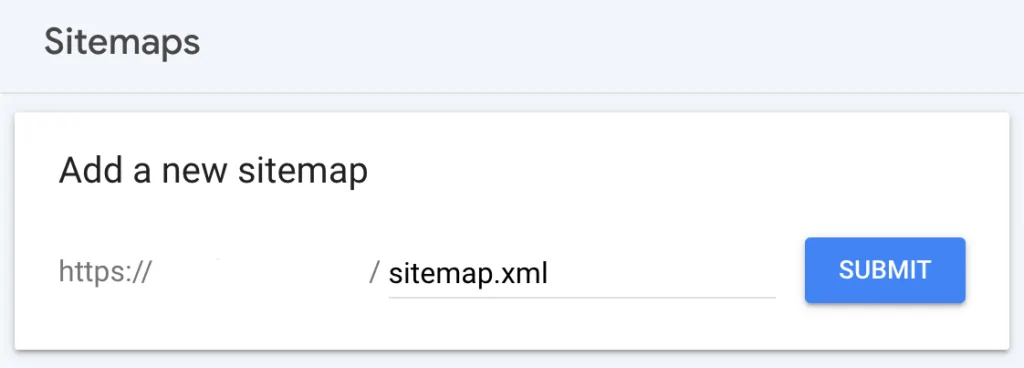
- Submit the Sitemap:
- Log into Google Search Console.
. - Navigate to the Sitemaps section under the Index tab.
. - Enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g.,
https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml).
. - Click the Submit button.
.
- Log into Google Search Console.
After submitting your sitemap, Google will regularly revisit it to discover new pages or changes.
To enhance your sitemap’s effectiveness, ensure it includes only high-quality, indexable pages.
Exclude irrelevant pages like admin login pages or duplicate content.
3. Structure Your Site Properly
Google prioritizes websites with clear and logical structures.
A well-structured site not only improves user experience but also makes it easier for Google’s crawlers to navigate and index content effectively.
Best Practices for Structuring Your Site:
- Adopt a Hierarchical Structure:
Organize your website into a logical hierarchy:
.- Homepage: The top-level page linking to all key categories.
. - Categories and Subcategories: Group related content under broader topics.
. - Individual Pages: Each page should cover a specific topic and link back to its category.
.
- Homepage: The top-level page linking to all key categories.
- Include Breadcrumb Navigation:
Breadcrumbs help users and crawlers understand the site’s structure by showing the path to a particular page.
For instance: Home > Blog > SEO Tips.
. - Optimize URLs:
Use descriptive, concise URLs that include keywords.
For example, replacehttps://yourwebsite.com/p123withhttps://yourwebsite.com/seo-tips.
.
By organizing your site effectively, you not only assist Google in indexing but also improve user engagement, which can indirectly boost rankings.
4. Build Backlinks to Your Site
Backlinks are one of the most powerful signals that tell Google your website is credible and worth indexing.
When Google discovers your links on other websites, it can prioritize crawling your pages faster.
However, focus on obtaining quality backlinks from authoritative sources.
Strategies to Build Backlinks:
- Guest Blogging:
Write insightful articles for reputable blogs in your industry. Include a link to your website within the content or author bio.
. - Resource Outreach:
Identify websites that feature resource lists in your niche and pitch your content or tools as valuable additions.
. - Social Media Sharing:
Share your site’s content on platforms like Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook.
While these links are often “nofollow,” they can still drive traffic and visibility, increasing the chances of earning natural backlinks.
. - Collaborate with Influencers:
Partner with influencers or thought leaders in your niche to share or link to your content.
. - Create Shareable Content:
Publish high-quality resources like infographics, case studies, or guides that naturally attract backlinks.
.
Remember, building backlinks is an ongoing process.
Avoid using black-hat SEO tactics like buying links, as this could result in penalties from Google.
Focus instead on establishing genuine relationships and creating valuable content that others want to link to.
Still Not Indexed? Check for Deeper Issues
If your site still isn’t indexed, it’s time to dig into technical or content-related issues.
These issues often prevent Google from crawling, indexing, or understanding your website.
Troubleshooting them can significantly improve your chances of appearing in search results.
Here’s a detailed guide on how to address some common problems:
1. Check for Rogue “noindex” Tags
A noindex tag in your website’s code explicitly tells Google not to index a page.
While these tags are useful for private, test, or duplicate pages, they can accidentally block important content if misused.
How to Check:
- Use the Inspect Element tool in your browser to view the HTML source of the page.
Right-click on the page and select “Inspect” or pressCtrl + Shift + I(Cmd + Option + Ion Mac).
. - Search the HTML code for the following meta tag:
.<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
.
- If this tag exists on critical pages, it’s preventing Google from indexing them.
.
Solution:
- Remove
noindextags from any pages you want to appear in search results.
. - Ensure your robots.txt file doesn’t block Googlebot from accessing these pages, as this could prevent Google from seeing the updated meta tags.
.
2. Check for Manual Actions and Security Issues
Google may impose manual penalties if your website violates its guidelines, such as engaging in spammy practices or having poor-quality content.
Similarly, security issues like malware can make Google exclude your site to protect users.
Steps to Resolve:
- Log in to Google Search Console and navigate to the Manual Actions section.
.- Look for any warnings or penalties that might affect your site. Common reasons include unnatural backlinks, thin content, or spammy practices.
.
- Look for any warnings or penalties that might affect your site. Common reasons include unnatural backlinks, thin content, or spammy practices.
- Check the Security Issues section for malware warnings or other vulnerabilities.
. - If there are manual actions or security flags, follow the provided steps to fix the issues. For example:
.- Remove malicious scripts, fix hacked content, or clean up unnatural backlinks.
.
- Remove malicious scripts, fix hacked content, or clean up unnatural backlinks.
- Once resolved, submit a Reconsideration Request through Search Console to notify Google that your site complies with its guidelines.
.
3. Check That Your Content is Valuable
Google prioritizes indexing content that provides value to users.
Pages with low-quality, duplicate, or irrelevant content are less likely to be indexed.
Tips to Improve Content:
- Focus on Originality: Write unique, in-depth content that addresses the specific needs or queries of your target audience.
Avoid simply copying or rewriting existing content.
. - Use Clear Structure: Divide your content with headers, subheaders, bullet points, and images to enhance readability.
. - Target User Intent: Research what users are searching for in your niche and tailor your content to provide solutions.
. - Add Rich Media: Include videos, infographics, and images to make your content engaging and increase its value to visitors.
.
Additionally, update outdated pages with fresh information to ensure relevance.
4. Check for Indexable Pages Not in Your Sitemap
Google relies heavily on sitemaps to find and crawl pages on your site.
If a page isn’t in your sitemap, it might not be indexed.
Solution:
- Compare your live website pages with the URLs in your sitemap using tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs.
. - Ensure all important pages are included in the sitemap.
. - Submit the updated sitemap to Google via Google Search Console.
.
Regularly updating your sitemap and resubmitting it ensures Google has access to all indexable pages.
5. Check for Rogue Canonical Tags
Canonical tags signal to Google which version of a page to index when there are multiple versions (e.g., http vs. https, or parameterized URLs).
Misconfigured canonical tags can unintentionally point away from the desired page.
How to Fix:
- Use the View Page Source option in your browser to inspect the
<link rel="canonical">tag.
. - Verify that the canonical URL points to the correct version of the page.
.- For instance, a canonical tag on
https://example.com/pageshould not point to another page unless intentional.
.
- For instance, a canonical tag on
- Remove or correct incorrect canonical tags to prevent indexing errors.
.
6. Check for “nofollow” Internal Links
Internal links with the nofollow attribute tell Google not to follow or index the linked pages.
Overuse or improper use of nofollow can hinder the discovery of important content.
Solution:
- Use tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to audit your site’s internal links.
. - Identify critical pages linked internally with
nofollowattributes.
> - Replace
nofollowwith standard links for pages that you want indexed.
.
Proper internal linking can also enhance the flow of link equity across your site, boosting SEO.
7. Check for Internal Link Opportunities
Internal linking isn’t just about navigation; it’s also a way for Google to understand the structure and hierarchy of your site.
Best Practices:
- Link to High-Value Pages: Ensure critical pages (e.g., cornerstone content, product pages) are linked from your homepage or other high-traffic pages.
. - Use Descriptive Anchor Text: Include relevant keywords in the anchor text to give context about the linked page’s content.
. - Balance Link Distribution: Avoid overloading certain pages with excessive internal links while neglecting others.
.
Building a robust internal linking strategy helps Google crawl and index your pages more effectively.
8. Check for Crawl Budget Issues
Crawl budget refers to the number of pages Googlebot can or will crawl on your site during a specific period.
Low-value or excessive pages can waste this budget, leaving critical content uncrawled.
Steps to Optimize:
- Identify Low-Value Pages: Use SEO tools to find thin content, duplicate pages, or irrelevant sections (e.g., tag archives).
. - Consolidate Content: Merge similar pages to create comprehensive resources.
. - Block Irrelevant Pages: Use the
robots.txtfile ornoindexmeta tags to prevent Google from crawling unnecessary pages, such as admin or test pages.
.
Additionally, ensure your site’s speed and server response times are optimized, as slow performance can limit crawl efficiency.
By addressing these issues, you can significantly improve your site’s chances of being indexed and performing well in search results.
Regular monitoring and optimization will ensure long-term success.
Final Thoughts
Getting indexed by Google is essential for driving organic traffic to your website.
Without proper indexing, even the most informative and engaging content will remain invisible to search engine users.
By implementing these strategies—ranging from submitting sitemaps to ensuring your content meets quality standards—you can significantly improve your chances of being indexed.
Once indexed, your pages can start appearing in search results, opening the door to increased visibility and audience engagement.
However, remember that indexing is just the first step in the larger process of SEO success.
To truly thrive, focus on creating consistent value for your audience by understanding their needs and delivering content that addresses their pain points or interests.
Additionally, optimize your site’s user experience to encourage visitors to stay longer and explore further.
Combine these efforts with a commitment to continuously refining your SEO strategy, and you’ll be well on your way to building a robust online presence and achieving sustainable growth.


![How to Use LinkedIn for Business [2025 Guide]](https://technaseer.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/download-300x156.png)

![How to Build a LinkedIn Marketing Strategy [Free Template]](https://technaseer.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/1696446402112-300x169.jpeg)

